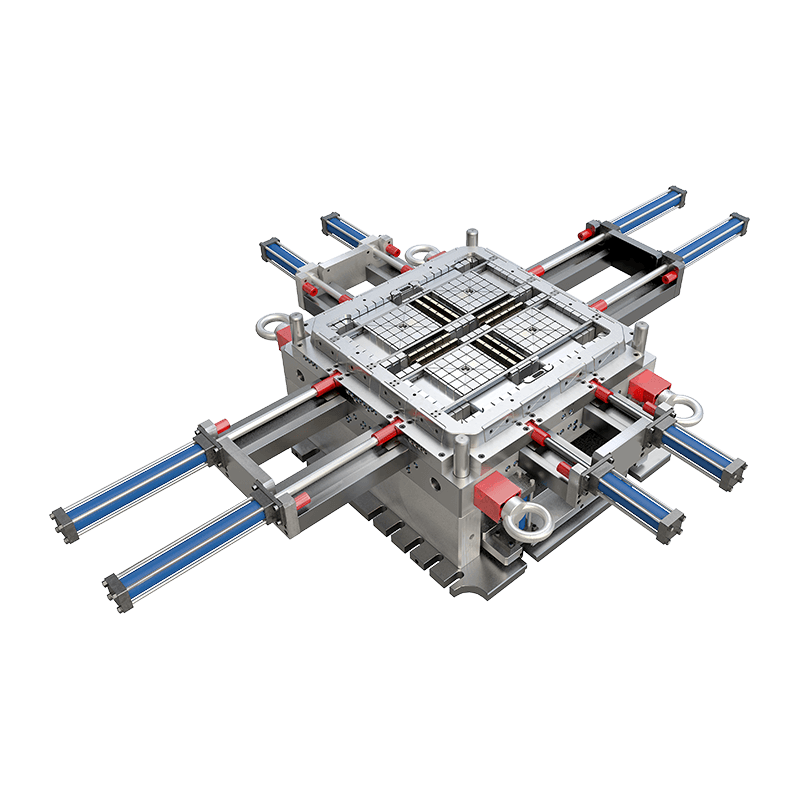
The design of cooling systems for Plastic Industrial Tray Mould is a critical aspect of the mold-making process. Efficient cooling is essential for the production of high-quality plastic trays, as it directly impacts the cycle time, part quality, and overall productivity of the mold. The cooling system must be designed to remove heat from the mold quickly and evenly to ensure that the plastic material cools uniformly, preventing warping and other defects.
In the realm of Plastic Industrial Tray Mould design, the cooling system is often an afterthought, but it should be a primary consideration. The cooling system is responsible for dissipating the heat generated during the injection molding process, which can reach temperatures of several hundred degrees Celsius. If the heat is not effectively managed, it can lead to prolonged cooling times, reduced production rates, and potentially warped or distorted trays.
The design of the cooling system for a Plastic Industrial Tray Mould begins with an understanding of the material being used and the geometry of the mold. The mold's cooling channels must be strategically placed to ensure that heat is extracted from the mold's core and cavity uniformly. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining the dimensional stability of the mold and the quality of the plastic trays produced.
One of the key considerations in the design of a Plastic Industrial Tray Mould's cooling system is the type of cooling channel used. Traditional straight channels are simple to manufacture but may not provide the most efficient heat transfer. More advanced designs, such as spiral or serpentine channels, can offer better heat dissipation by increasing the surface area in contact with the mold. However, these designs are more complex to manufacture and may require additional tooling and maintenance.
Another important aspect of the cooling system design is the use of cooling inserts. These inserts can be placed in specific areas of the mold where heat concentration is higher, providing targeted cooling and further improving the efficiency of the system. The materials used for these inserts can also impact the cooling performance, with materials like copper or aluminum offering better thermal conductivity than steel.
The integration of the cooling system with the overall design of the Plastic Industrial Tray Mould is also critical. The cooling channels must be designed in such a way that they do not interfere with the mold's core and cavity geometry, which could affect the shape and detail of the final plastic tray. This requires a careful balance between cooling efficiency and maintaining the mold's structural integrity.
Simulation software can be a valuable tool in the design process, allowing engineers to model the flow of coolant through the channels and predict the temperature distribution within the mold. This can help identify areas where the cooling system may be insufficient and guide the optimization of the design.
Maintenance of the cooling system is also a critical factor in the performance of a Plastic Industrial Tray Mould. Over time, the channels can become clogged with debris or scale, reducing their effectiveness. Regular cleaning and inspection of the cooling system can help ensure that it continues to operate at peak efficiency.
In conclusion, the design of the cooling system for a Plastic Industrial Tray Mould is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of the materials, geometry, and manufacturing processes involved. By carefully considering the placement, design, and materials of the cooling channels, as well as the integration of the cooling system with the overall mold design, manufacturers can ensure that their Plastic Industrial Tray Moulds produce high-quality plastic trays with minimal defects and maximum efficiency.